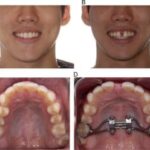
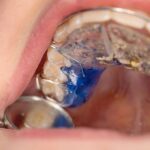
Metal expander is a mechanical device used in various industries to expand or stretch metal components. It is commonly used in manufacturing processes to increase the size or shape of metal parts, such as tubes, pipes, or sheets. The metal expander works by exerting force on the metal, causing it to stretch and expand.
How does a metal expander work?
The metal expander consists of a series of rollers or mandrels that are positioned in a specific arrangement. When the metal component is passed through these rollers, it is subjected to an external force, which causes it to stretch and expand. The rollers or mandrels can be adjusted to achieve the desired expansion or stretching of the metal.
What are the applications of a metal expander?
Metal expanders are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing. They are used to create metal components with specific dimensions and shapes. For example, in the automotive industry, metal expanders are used to create exhaust pipes with the desired diameter and length. In the aerospace industry, they are used to manufacture aircraft parts with precise dimensions.
Advantages of using a metal expander
Using a metal expander has several advantages. First, it allows for precise control over the expansion or stretching of metal components, ensuring that they meet the required specifications. Second, it is a cost-effective method compared to other techniques such as forging or casting. Third, it is a versatile tool that can be used with various types of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper.
Metal Expander: The Ultimate Guide
The functionality of a metal expander is based on the principle of controlled mechanical force applied to expand the diameter of a metal tube or pipe. It is used to increase the internal diameter of the tube or pipe, allowing for better flow and improved performance in various applications. The expansion process involves stretching the metal material, which can be achieved through different methods such as hydraulic pressure, mechanical force, or thermal expansion.
The expansion process starts by inserting the metal tube or pipe into the expander. The expander then applies force to the inner surface of the tube or pipe, causing it to expand. The force can be applied uniformly or selectively, depending on the desired expansion pattern. The expansion can be done in a single step or in multiple steps, depending on the required level of expansion and the properties of the metal material.
During the expansion process, the metal material undergoes plastic deformation, which permanently changes its shape. This deformation allows for the expansion of the tube or pipe without causing any damage or weakening of the material. The expanded tube or pipe retains its structural integrity and can withstand the operating conditions and pressures of the application it is used in.
The functionality of a metal expander is crucial in various industries where precise and controlled expansion of metal tubes or pipes is required. It ensures the efficient operation and performance of systems such as heat exchangers, condensers, boilers, and refrigeration systems.
Key Components of a Metal Expander
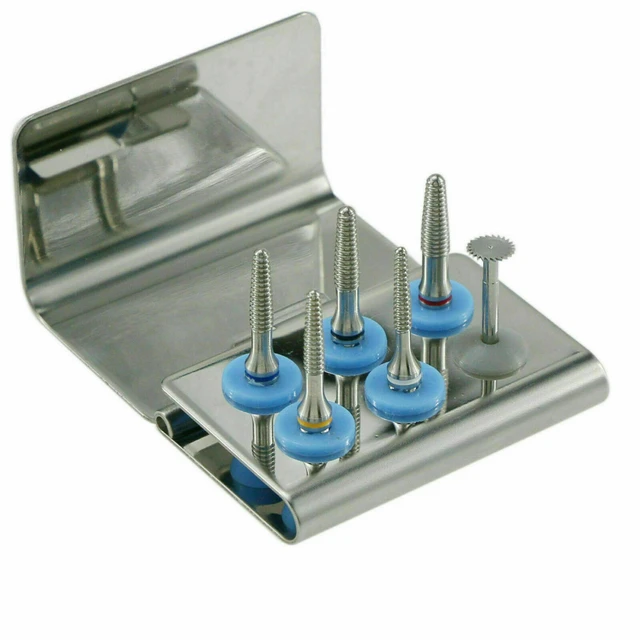

A metal expander consists of several key components that work together to achieve the desired expansion of metal tubes or pipes. These components include:
- Expander Head: The expander head is the main component responsible for applying the force to the inner surface of the tube or pipe. It is designed to exert controlled and uniform pressure to achieve the desired expansion.
- Expander Mandrel: The expander mandrel is a cylindrical rod or shaft that supports the inner surface of the tube or pipe during the expansion process. It helps to maintain the shape and integrity of the tube or pipe while it is being expanded.
- Expansion Dies: The expansion dies are used to shape the metal material during the expansion process. They come in various sizes and shapes to accommodate different tube or pipe diameters and expansion requirements.
- Hydraulic System: The hydraulic system provides the necessary force to the expander head. It consists of a hydraulic pump, cylinders, valves, and hoses that work together to generate and control the hydraulic pressure.
- Control System: The control system is responsible for monitoring and controlling the expansion process. It includes sensors, actuators, and a control panel that allow operators to set and adjust the desired expansion parameters.
These key components work together to ensure the precise and controlled expansion of metal tubes or pipes, resulting in improved performance and efficiency in various applications.
A metal expander is a mechanical device that is used to increase the size or dimensions of metal objects. It works by applying force or pressure to the metal, causing it to expand or stretch. This process is commonly used in various industries, such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive, to achieve the desired shape and size of metal components.
The functionality of a metal expander relies on the principle of elasticity. When force or pressure is applied to a metal object, the atoms within the metal start to move and rearrange themselves. This movement causes the metal to stretch or expand, increasing its size and dimensions. The metal expander is designed to apply controlled and precise force to achieve the desired expansion without damaging the metal.
Key components of a metal expander include:
- Frame: The frame provides the structure and support for the metal expander.
- Hydraulic or mechanical system: This system generates the force or pressure required for the expansion process.
- Expansion tooling: The expansion tooling is the part of the metal expander that comes into direct contact with the metal object and applies the force or pressure for expansion.
- Control system: The control system allows the operator to adjust and monitor the force, speed, and other parameters of the expansion process.
Types of metal expanders:
- Hydraulic metal expanders: These metal expanders use hydraulic pressure to apply force and expand the metal. They are commonly used for heavy-duty applications.
- Mechanical metal expanders: These metal expanders use mechanical force, such as screws or levers, to expand the metal. They are often used for smaller-scale applications.
Benefits of using metal expanders:
- Precision: Metal expanders allow for precise control over the expansion process, ensuring accurate dimensions and shapes.
- Efficiency: Metal expanders can quickly and efficiently expand metal objects, reducing the time and labor required for manual stretching or resizing.
- Versatility: Metal expanders can be used on various types of metal, including steel, aluminum, and copper.
- Cost-effectiveness: By eliminating the need for manual resizing or purchasing new metal components, metal expanders can help save costs in the long run.
Applications of metal expanders:
- Tube expansion: Metal expanders are commonly used in industries such as HVAC, refrigeration, and plumbing to expand tubes for better heat transfer or joining.
- Sheet metal forming: Metal expanders can be used to stretch or shape sheet metal for various applications, such as automotive body panels or industrial components.
- Pipe fitting: Metal expanders are used in pipe fitting applications to expand pipes for better connections or to repair damaged sections.
Factors to consider when choosing a metal expander:
- Capacity: Consider the maximum size and dimensions of metal objects that the expander can handle.
- Force and pressure: Evaluate the force and pressure capabilities of the expander to ensure it meets the requirements of your specific application.
- Control features: Look for an expander with adjustable control features to allow for precise and customized expansion processes.
- Reliability and durability: Choose a metal expander that is built to withstand heavy-duty use and has a reputation for reliability.
Maintenance and care for metal expanders:
- Regular inspection: Conduct routine inspections of the expander to check for any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction.
- Cleaning: Keep the expander clean from dust, debris, and any other contaminants that may affect its performance.
- Lubrication: Apply lubrication to the moving parts of the expander to ensure smooth operation and prevent friction.
- Proper storage: Store the expander in a clean and dry environment to prevent rust or corrosion.
Common issues and troubleshooting:
- Uneven expansion: If the metal object is expanding unevenly, check for any misalignment or damage in the expansion tooling.
- Insufficient expansion: If the metal object is not expanding enough, check the force and pressure settings of the expander and adjust accordingly.
- Overexpansion: If the metal object is expanding beyond the desired dimensions, reduce the force or pressure applied by the expander.
- Malfunctioning control system: If the control system is not functioning properly, check for any loose connections or faulty components.
Future trends in metal expander technology:
- Automation: Metal expanders are likely to become more automated, with advanced control systems and robotics for increased efficiency and precision.
- Smart technology: Metal expanders may incorporate smart technology, such as sensors and data analytics, to optimize the expansion process and improve performance.
- Energy efficiency: Future metal expanders may focus on energy-efficient designs and technologies to reduce power consumption and environmental impact.
- Integration with other processes: Metal expanders may be integrated with other manufacturing processes, such as welding or cutting, to streamline production and reduce costs.
Key Components of a Metal Expander
1. Frame
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/ca/1×1.png
The frame of a metal expander provides the structural support and stability needed to handle the high forces and pressures involved in the expansion process. It is typically made of durable materials such as steel or aluminum to ensure long-lasting performance.
2. Expansion Chamber
The expansion chamber is where the actual expansion of the metal takes place. It is a sealed chamber that can withstand high temperatures and pressures. The metal to be expanded is placed inside the chamber, and the necessary heat and pressure are applied to achieve the desired expansion.
3. Heating System
The heating system is responsible for providing the necessary heat to the expansion chamber. It can use various heat sources, such as electric heaters or gas burners, depending on the specific requirements of the metal being expanded. The heating system must be capable of reaching and maintaining the desired temperature throughout the expansion process.
4. Cooling System
The cooling system is used to rapidly cool the expanded metal after the expansion process is complete. This is necessary to ensure that the metal retains its desired shape and properties. The cooling system can use methods such as water quenching or air cooling, depending on the specific requirements of the metal being expanded.
5. Control System
The control system is the brain of the metal expander. It is responsible for monitoring and controlling various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and expansion rate. It ensures that the expansion process is carried out accurately and safely. The control system may include sensors, actuators, and a user interface for easy operation and adjustment.
Types of Metal Expanders
1. Tube Expanders
Tube expanders are widely used in the HVAC, refrigeration, and heat exchanger industries. They are designed to expand the ends of tubes to ensure a secure and leak-free connection. Tube expanders come in different sizes and configurations to accommodate various tube diameters and materials.
2. Flaring Tools
Flaring tools are used to create flares on the ends of pipes or tubes. These flares provide a secure connection when joining pipes or attaching fittings. Flaring tools are commonly used in plumbing, automotive, and hydraulic applications.
3. Swaging Tools
Swaging tools are used to reduce the diameter of pipes or tubes. They work by compressing the material, creating a smaller diameter at the swaged end. Swaging tools are commonly used in the plumbing, HVAC, and automotive industries.
4. Ring Expanders
Ring expanders are specifically designed to expand the inner diameter of rings, such as piston rings or sealing rings. They are commonly used in the automotive and manufacturing industries to ensure a proper fit and seal.
5. Mandrels
Mandrels are cylindrical tools used to support and shape the workpiece during the expansion process. They are commonly used in tube expansion and pipe bending applications. Mandrels come in various sizes and materials to accommodate different workpiece dimensions and materials.
6. Roller Expanders
Roller expanders are used to expand the diameter of tubes or pipes by rolling over them with a set of rollers. This method is often used in the heat exchanger and boiler industries to achieve a uniform expansion without causing any damage to the material.
These are just a few examples of the types of metal expanders available. Each type has its own unique features and applications. When choosing a metal expander, consider the specific requirements of your project and consult with experts or manufacturers to ensure you select the right tool for the job.
Benefits of Using Metal Expanders
1. Increased Efficiency:
Metal expanders are designed to efficiently expand metal tubes, allowing for improved heat transfer and enhanced performance of heat exchangers and other equipment. By increasing the surface area of the tubes, metal expanders help optimize the efficiency of the system, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs.
2. Enhanced Durability:
Metal expanders are typically made from high-quality materials such as stainless steel or hardened alloy, which ensures their durability and longevity. They are designed to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions, making them suitable for use in demanding industrial environments. The robust construction of metal expanders allows them to withstand heavy use and resist wear and tear, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
3. Versatility:
Metal expanders are available in various sizes and configurations, making them versatile tools that can be used in a wide range of applications. Whether you need to expand small-diameter tubes or large-diameter pipes, there is a metal expander available to meet your specific requirements. This versatility makes metal expanders a valuable asset in industries such as HVAC, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
4. Cost Savings:
By using metal expanders, industries can achieve significant cost savings in multiple ways. Firstly, the increased efficiency of heat exchangers and other equipment results in reduced energy consumption, translating into lower utility bills. Secondly, the durability and longevity of metal expanders minimize the need for frequent replacements or repairs, saving on maintenance costs. Lastly, the versatility of metal expanders allows for a single tool to be used in multiple applications, reducing the need for investing in different tools for different tasks.
5. Improved Product Quality:
When metal tubes are expanded using metal expanders, it ensures a tight and secure fit, resulting in improved product quality. The expanded tubes provide better heat transfer, which is crucial in applications where precise temperature control is required. Additionally, the secure fit of the expanded tubes prevents leaks and ensures the integrity of the system, contributing to the overall reliability and performance of the equipment.
Overall, the benefits of using metal expanders make them an indispensable tool in various industries. From increased efficiency and enhanced durability to cost savings and improved product quality, metal expanders offer a range of advantages that contribute to the success and productivity of industrial operations.
Applications of Metal Expanders
Metal expanders have a wide range of applications across various industries. Their ability to expand and contract metal materials makes them invaluable in many processes. Here are some of the key applications of metal expanders:
1. Heat Exchangers
Metal expanders are commonly used in heat exchangers to increase the surface area of the heat transfer tubes. By expanding the tubes, the heat exchanger can achieve a higher heat transfer efficiency, resulting in improved performance and energy savings.
2. Tube Expansion
Metal expanders are widely used in tube expansion applications, such as in the manufacturing of boilers, condensers, and heat exchangers. They are used to expand the tubes, ensuring a tight and secure fit between the tubes and the tube sheets, enhancing the overall structural integrity.
3. Automotive Industry
Metal expanders find extensive use in the automotive industry for various applications. They are used in the manufacturing of exhaust systems, mufflers, and catalytic converters. Metal expanders help in creating a tight seal between the different components, ensuring optimal performance and reducing the risk of leaks.
4. Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, metal expanders are used for tube expansion in heat exchangers, boilers, and condensers. They are also used in the production of pipes and fittings, ensuring a secure and reliable connection between the different components.
5. Aerospace Industry
Metal expanders play a vital role in the aerospace industry. They are used in the manufacturing of aircraft engines, heat exchangers, and various other components. Metal expanders help in achieving precise fits and tight connections, ensuring the safety and efficiency of the aerospace equipment.
6. Power Generation
Metal expanders are widely used in power generation plants, including thermal power plants and nuclear power plants. They are used for tube expansion in boilers, condensers, and heat exchangers, ensuring efficient heat transfer and reliable operation of the power generation equipment.
7. HVAC Systems
Metal expanders are essential in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) industry. They are used in the manufacturing of air conditioning units, refrigeration systems, and heat pumps. Metal expanders help in creating a tight seal between the different components, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
8. Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, metal expanders are used for tube expansion in various equipment, such as pharmaceutical reactors and heat exchangers. They help in maintaining the integrity of the equipment, ensuring efficient heat transfer and preventing any contamination.
These are just a few examples of the applications of metal expanders. Their versatility and reliability make them an essential tool in various industries where precision, efficiency, and durability are paramount.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Metal Expander
When choosing a metal expander, there are several important factors that need to be considered. These factors will help determine the suitability of the expander for your specific requirements and ensure optimal performance. Here are some key factors to consider:
3. Speed and Efficiency: The speed and efficiency of the metal expander are important factors to consider, especially if you have specific production targets or time constraints. Look for an expander that offers high-speed operation and efficient performance to maximize productivity.
4. Durability and Longevity: The durability and longevity of the metal expander are crucial considerations, especially if you are planning to use it in a demanding or harsh environment. Look for an expander that is made from high-quality materials and has a robust construction to ensure long-lasting performance.
6. Safety Features: Safety is a paramount concern when choosing a metal expander. Look for features such as overload protection, emergency stop buttons, and safety interlocks to ensure the safety of operators and prevent accidents or damage.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability: Consider the maintenance and service requirements of the metal expander. Look for features such as easy access to components, user-friendly interfaces, and availability of spare parts to ensure convenient maintenance and minimize downtime.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right metal expander for your specific needs and ensure optimal performance and reliability. Remember to consult with experts or manufacturers for additional guidance and support.
Maintenance and Care for Metal Expanders
Metal expanders are precision instruments that require regular maintenance and care to ensure optimal performance and longevity. By following proper maintenance procedures, you can prevent issues and prolong the lifespan of your metal expander.
1. Cleaning: Regular cleaning is essential to remove dirt, debris, and any other contaminants that may accumulate on the surface of the metal expander. Use a soft cloth or brush to gently wipe away any particles. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or solvents that can damage the surface of the expander.
2. Lubrication: Metal expanders have moving parts that require lubrication to reduce friction and ensure smooth operation. Apply a small amount of lubricating oil to the designated areas as recommended by the manufacturer. Be careful not to over-lubricate, as excess oil can attract dust and dirt.
3. Inspection: Regular inspection of the metal expander is crucial to identify any signs of wear or damage. Check for loose screws, cracks, or any other abnormalities. If you notice any issues, contact the manufacturer or a qualified technician for repair or replacement.
5. Calibration: Metal expanders may require periodic calibration to ensure accurate measurements. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for calibration procedures or consult a professional calibration service. Regular calibration will help maintain the precision and accuracy of your metal expander.
6. Training: Proper training is essential for anyone using a metal expander. Ensure that operators are familiar with the functionality and safety precautions of the specific model they are using. This will help prevent misuse and minimize the risk of damage to the expander or injury to the operator.
7. Documentation: Keep a record of all maintenance and calibration activities performed on your metal expander. This documentation will serve as a reference and help track the history of the instrument. It can also be useful for warranty purposes or when troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
By following these maintenance and care guidelines, you can ensure that your metal expander remains in optimal condition and continues to provide accurate and reliable results. Regular maintenance will not only extend the lifespan of the instrument but also contribute to the overall efficiency and productivity of your operations.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
1. Lack of Expansion
2. Excessive Noise
3. Leakage
Leakage is another common issue that may occur with metal expanders. This can be caused by worn-out seals or gaskets. In such cases, replacing the damaged seals or gaskets can help resolve the leakage problem. It is also essential to ensure that the expander is properly tightened to prevent any leaks. Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify and address any potential leakage issues.
4. Overheating
If the metal expander is overheating during operation, it is crucial to identify and address the underlying cause promptly. Overheating can be caused by several factors, such as excessive friction, inadequate lubrication, or a malfunctioning cooling system. Checking the lubrication levels, ensuring proper alignment, and inspecting the cooling system can help prevent overheating. If the issue persists, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer or a professional technician for further assistance.
5. Inconsistent Performance
Future Trends in Metal Expander Technology
1. Advanced Materials

2. Miniaturization
Another trend in metal expander technology is the miniaturization of expanders. As industries continue to demand smaller, more compact equipment, metal expanders are being designed to fit into tighter spaces without compromising their performance. This trend is particularly important in industries such as aerospace and medical, where space is often limited.
3. Integration with IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing various industries, and metal expander technology is no exception. Metal expanders can now be equipped with sensors and connected to IoT platforms, allowing for real-time monitoring and data analysis. This integration enables predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and optimization of metal expander performance.
4. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a growing concern in many industries, and metal expander technology is being developed to address this challenge. Future metal expanders will be designed to minimize energy consumption while maximizing output. This may involve the use of advanced control systems, improved heat transfer mechanisms, and optimized designs to reduce energy losses.
5. Automation and Robotics
The automation and robotics revolution is expected to have a significant impact on metal expander technology. As industries increasingly adopt automated processes, metal expanders will be integrated into these systems to enhance productivity and efficiency. This may involve the use of robotic arms, automated loading and unloading systems, and advanced control algorithms.
6. Enhanced Performance
Advancements in technology will continue to push the boundaries of metal expander performance. Future metal expanders will be capable of handling higher pressures, temperatures, and flow rates, allowing for greater versatility and adaptability in various applications. These advancements will enable industries to achieve higher productivity and efficiency levels.

Dr. Fidel Cann: Esteemed orthodontist with a lifelong dedication to enhancing smiles and oral health. Pioneering expertise, compassionate care.