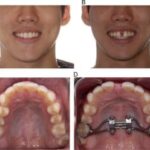
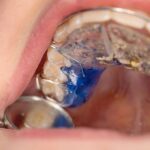
An EFDH is a dental hygienist who has undergone additional training and certification to perform advanced procedures beyond the scope of a traditional dental hygienist. These procedures may include placing fillings, administering local anesthesia, and taking dental impressions, among others. By expanding their skill set, EFDHs are able to assist dentists in providing a wider range of dental treatments.
One of the main benefits of having an EFDH on the dental team is that it allows for more efficient and streamlined dental care. With an EFDH, dental offices can offer a one-stop-shop for patients, eliminating the need for them to visit multiple providers for different procedures. This not only saves patients time and effort but also ensures that their oral health needs are met effectively and comprehensively.
What is an Expanded Function Dental Hygienist?
An Expanded Function Dental Hygienist (EFDH) is a dental professional who has received additional training and education to perform advanced dental procedures. They work under the supervision of a dentist and play a crucial role in the delivery of oral healthcare services.
The main goal of an EFDH is to provide comprehensive dental care to patients, focusing on preventive and therapeutic treatments. They work closely with dentists to develop treatment plans and ensure that patients receive the highest level of care.
Expanded Function Dental Hygienists are trained to perform a wide range of procedures, including but not limited to:
| Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Dental cleanings | Removing plaque and tartar buildup from teeth |
| Scaling and root planing | Deep cleaning of the gums to treat gum disease |
| Administering local anesthesia | Numbing the area before dental procedures |
| Applying dental sealants | Protecting teeth from decay by applying a thin plastic coating |
| Fluoride treatments | Strengthening teeth and preventing cavities |
| Oral health education | Teaching patients about proper oral hygiene practices |
Expanded Function Dental Hygienists are an essential part of the dental team and contribute to the overall oral health of patients. They work in various settings, including private dental offices, community health clinics, and public health departments.
To become an Expanded Function Dental Hygienist, individuals must complete additional education and training beyond the requirements for a traditional dental hygienist. This typically includes completing a specialized program or earning a degree in dental hygiene with an expanded functions component.
Overview of Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
An Expanded Function Dental Hygienist (EFDH) is a specialized dental professional who has received additional training and education to perform advanced dental procedures. EFDHs work under the supervision of a dentist and play a crucial role in providing comprehensive oral care to patients.
Educational Requirements
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/ca/1×1.png
To become an EFDH, individuals must first complete a dental hygiene program and obtain a license as a dental hygienist. After gaining experience in the field, they can then pursue additional education and training in expanded functions.
The specific educational requirements for EFDHs vary by state, but typically include completing an accredited expanded functions program. These programs cover topics such as dental anatomy, radiography, dental materials, and advanced clinical techniques.
Once the educational requirements are met, EFDHs must pass a state board examination to become certified in their expanded functions. This certification allows them to legally perform the advanced procedures within their scope of practice.
Scope of Practice
The scope of practice for EFDHs varies depending on state regulations and the specific duties delegated by the supervising dentist. However, common expanded functions may include placing and carving dental fillings, placing and removing periodontal dressings, and performing certain orthodontic procedures.
EFDHs may also be responsible for taking dental impressions, applying sealants, administering local anesthesia, and providing patient education on oral hygiene and preventive care.
Benefits of EFDHs
Having EFDHs as part of a dental practice can provide numerous benefits. These professionals are trained to perform advanced procedures, which can help to increase efficiency and productivity in the dental office.
By delegating certain tasks to EFDHs, dentists can focus on more complex procedures, allowing for better patient care and overall practice management. EFDHs also play a vital role in preventive dentistry, educating patients on proper oral hygiene practices and helping to prevent dental diseases.
Career Opportunities
The demand for EFDHs is growing, and there are various career opportunities available in both private dental practices and public health settings. EFDHs may also find employment in dental schools, research institutions, and dental product companies.
With their advanced skills and knowledge, EFDHs have the potential to earn competitive salaries and enjoy a rewarding career in the dental field. Continued education and professional development are essential for staying current with the latest advancements in dental hygiene and expanding their scope of practice.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Ability to perform advanced dental procedures | Varied scope of practice depending on state regulations |
| Increased efficiency and productivity in the dental office | Additional education and training required |
| Opportunities for career growth and development | Responsibility to stay current with advancements in dental hygiene |
Educational Requirements for Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
To become an Expanded Function Dental Hygienist (EFDH), individuals must meet specific educational requirements. These requirements ensure that EFDHs are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to perform their duties effectively and safely.
1. Completion of Dental Hygiene Program

The first step towards becoming an EFDH is to complete a dental hygiene program accredited by the Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA). These programs are typically offered at community colleges, universities, or technical schools and usually take about two years to complete.
During the dental hygiene program, students learn about oral anatomy, dental radiography, oral pathology, periodontal therapy, and other essential subjects. They also gain hands-on experience through clinical rotations, where they work under the supervision of licensed dental hygienists and dentists.
2. State-Specific Training
After completing a dental hygiene program, aspiring EFDHs must undergo additional training specific to their state’s requirements. Each state has its own set of rules and regulations regarding the scope of practice for EFDHs.
This state-specific training may involve attending workshops, seminars, or continuing education courses that focus on the expanded functions and responsibilities of EFDHs. It ensures that EFDHs are knowledgeable about the latest techniques, technologies, and guidelines in their field.
3. Certification or Licensure
Once the educational and state-specific training requirements are met, individuals can pursue certification or licensure as an EFDH. The specific requirements for certification or licensure vary by state.
In some states, EFDHs may need to pass a written and clinical examination administered by a state board or regulatory agency. These examinations assess the individual’s knowledge and skills related to expanded functions, such as administering local anesthesia, placing dental sealants, or performing restorative procedures.
After successfully obtaining certification or licensure, EFDHs must adhere to any continuing education requirements set by their state. This ensures that they stay up-to-date with advancements in dental hygiene and maintain their competence in performing expanded functions.
Scope of Practice for Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
An Expanded Function Dental Hygienist (EFDH) is a dental professional who has received additional training and education to perform certain dental procedures beyond the traditional role of a dental hygienist. The scope of practice for an EFDH may vary depending on state regulations and individual training, but generally includes the following:
1. Restorative Procedures:
An EFDH is trained to assist the dentist in performing restorative procedures, such as placing and contouring dental fillings, placing temporary crowns, and cementing permanent crowns.
2. Local Anesthesia Administration:
EFDHs are often trained to administer local anesthesia to patients prior to dental procedures. This allows for a more comfortable experience for the patient and enables the dentist to perform necessary treatments.
3. Dental Impressions:
EFDHs may be responsible for taking dental impressions, which are used to create models of a patient’s teeth for various purposes, such as creating custom dental appliances or evaluating orthodontic treatment progress.
4. Orthodontic Procedures:
In some states, EFDHs may be trained to perform certain orthodontic procedures, such as placing and adjusting orthodontic appliances, under the supervision of a dentist.
5. Periodontal Procedures:
EFDHs may perform periodontal procedures, including scaling and root planing, which involve removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots to treat gum disease.
6. Patient Education and Counseling:
7. Dental Radiography:
EFDHs are often trained to take dental x-rays, which are essential for diagnosing and treating dental conditions. They must follow strict safety protocols to ensure the well-being of the patient and themselves.
Benefits of Seeing an Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
One of the main benefits of seeing an EFDH is their expertise in performing various dental procedures. EFDHs have received additional education and training, which allows them to perform tasks beyond the scope of traditional dental hygienists. They are skilled in procedures such as placing dental sealants, administering local anesthesia, and performing certain restorative procedures under the supervision of a dentist.
By seeing an EFDH, patients can receive a more comprehensive level of care. These professionals are trained to identify and address oral health issues at an early stage, preventing them from progressing into more serious problems. They can provide personalized treatment plans and offer guidance on proper oral hygiene practices, helping patients maintain a healthy smile.
Another benefit of seeing an EFDH is the convenience they offer. With their expanded scope of practice, EFDHs can perform a wide range of procedures, reducing the need for referrals to other specialists. This means that patients can receive the majority of their dental care in one place, saving them time and effort.
Furthermore, seeing an EFDH can also have financial benefits. As EFDHs are able to perform certain restorative procedures, patients may be able to save money by avoiding the need for a separate appointment with a dentist. Additionally, EFDHs can help patients prevent costly dental issues by addressing problems early on, potentially saving them from more extensive and expensive treatments in the future.
Overall, seeing an Expanded Function Dental Hygienist can greatly benefit patients in terms of the level of care they receive, convenience, and potential cost savings. These highly trained professionals have the knowledge and skills to provide comprehensive preventive dentistry, helping patients achieve and maintain optimal oral health.
Role of Expanded Function Dental Hygienist in Preventive Dentistry
What is an Expanded Function Dental Hygienist?
An expanded function dental hygienist is a licensed dental hygienist who has received additional training and certification to perform certain dental procedures. They work under the supervision of a dentist and are authorized to perform advanced tasks beyond the scope of a traditional dental hygienist.
Scope of Practice for Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
The scope of practice for an expanded function dental hygienist may vary depending on state regulations, but generally includes the following procedures:
- Administering local anesthesia
- Placing and carving dental restorations
- Polishing and contouring dental restorations
- Placing and removing periodontal dressings
- Placing and removing temporary crowns
- Performing dental impressions
- Applying dental sealants
Benefits of Seeing an Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
Seeing an expanded function dental hygienist can provide several benefits for patients. EFDHs are trained to perform a wide range of preventive and restorative procedures, allowing them to provide comprehensive dental care. By working closely with dentists, they can help identify and address oral health issues early on, preventing more serious problems from developing.
EFDHs also play a crucial role in patient education. They can provide valuable information and guidance on oral hygiene practices, diet, and lifestyle habits that can contribute to oral health. By educating patients about proper oral care, EFDHs empower them to take control of their oral health and prevent dental problems.
Expanded Function Dental Hygienist vs Traditional Dental Hygienist
While traditional dental hygienists focus primarily on cleaning teeth and providing basic preventive care, expanded function dental hygienists have a broader scope of practice. They are trained to perform advanced procedures, such as administering local anesthesia and placing dental restorations. This allows them to provide more comprehensive care and assist dentists in providing a wider range of dental treatments.
Career Opportunities for Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
With their advanced training and skills, expanded function dental hygienists have a range of career opportunities available to them. They can work in private dental practices, community health centers, hospitals, and other dental care settings. Additionally, they may also choose to pursue further specialization in areas such as periodontics or pediatric dentistry.
Expanded Function Dental Hygienist vs Traditional Dental Hygienist
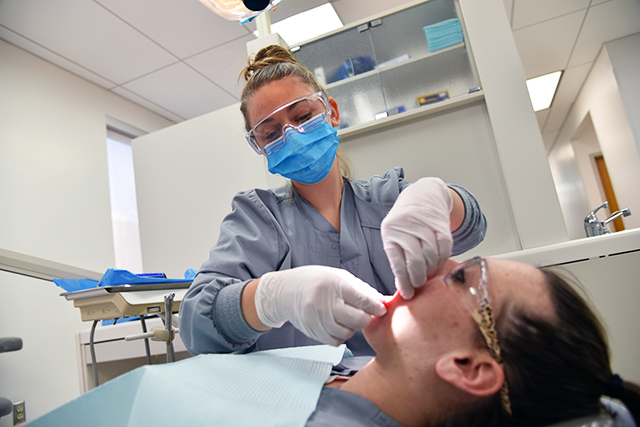
A traditional dental hygienist typically performs basic dental procedures such as teeth cleaning, taking X-rays, and educating patients on proper oral hygiene practices. They work closely with dentists to provide comprehensive care to patients.
On the other hand, an expanded function dental hygienist (EFDH) has received additional training and education to perform more advanced dental procedures. These procedures may include placing dental fillings, administering local anesthesia, and performing root planing and scaling. EFDHs work under the supervision of a dentist but have more autonomy in their practice.
One of the main benefits of seeing an EFDH is that they can provide a wider range of services compared to a traditional dental hygienist. This means that patients can receive more comprehensive care in one place, without the need for multiple appointments with different dental professionals.
Another advantage of EFDHs is that they can help improve access to dental care, especially in underserved areas. Since EFDHs can perform certain procedures that are typically done by dentists, they can help fill the gap in dental care availability and provide much-needed services to communities that may not have enough dentists.
| Expanded Function Dental Hygienist | Traditional Dental Hygienist |
|---|---|
| Performs advanced dental procedures | Performs basic dental procedures |
| Works under the supervision of a dentist | Works closely with dentists |
| Can provide a wider range of services | Provides basic dental services |
| Helps improve access to dental care | Assists in providing comprehensive care |
Career Opportunities for Expanded Function Dental Hygienist
As an expanded function dental hygienist, you have a wide range of career opportunities available to you. With your advanced training and skills, you can work in various settings within the dental field.
Private Dental Practices
Public Health Clinics
Public health clinics often focus on preventive dentistry, and as an expanded function dental hygienist, you will play a crucial role in promoting oral health and preventing dental diseases.
Specialty Dental Offices
Educational Institutions

If you have a passion for teaching and mentoring, you may consider a career in educational institutions. Many dental hygiene programs hire expanded function dental hygienists as instructors to train future dental professionals. You can share your knowledge and skills with aspiring dental hygienists, helping them develop the necessary competencies to succeed in their careers.
Research and Industry
For expanded function dental hygienists interested in research and development, there are opportunities in the dental industry. You can work for dental product manufacturers, conducting research, testing new products, and providing input on product development. This career path allows you to contribute to advancements in dental technology and improve patient care.
Overall, as an expanded function dental hygienist, you have a diverse range of career opportunities to choose from. Whether you prefer working in a private practice, public health setting, specialty office, educational institution, or dental industry, your advanced skills and knowledge will be in demand. Consider your interests and goals to determine the career path that aligns with your aspirations.

Dr. Fidel Cann: Esteemed orthodontist with a lifelong dedication to enhancing smiles and oral health. Pioneering expertise, compassionate care.