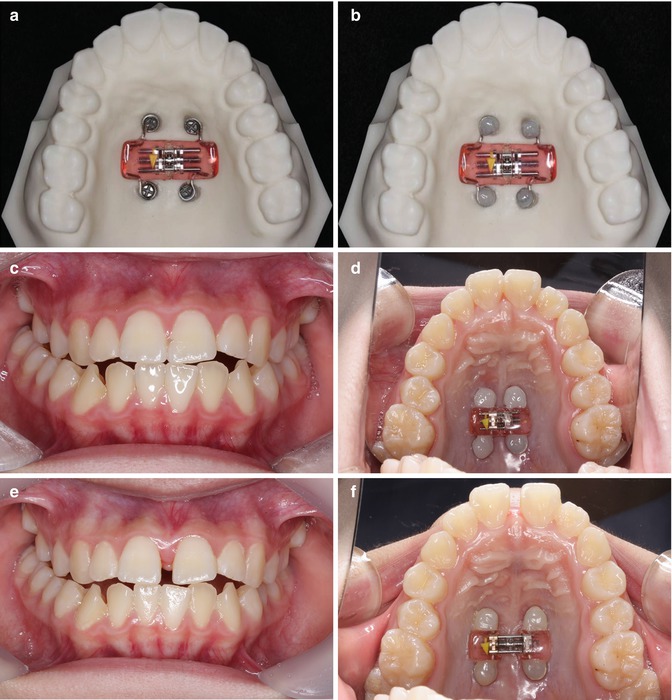
During the SAPE procedure, a surgeon makes small incisions in the patient’s palate and inserts a device called a palatal expander. The expander is then gradually adjusted over a period of time, applying gentle pressure to the palate and causing it to widen. This process allows the upper jaw to expand and create more room for the teeth to move into their correct positions.
One of the main benefits of SAPE is its ability to address skeletal discrepancies in patients with narrow palates. By surgically assisting the expansion of the upper jaw, orthodontists can achieve more stable and predictable results compared to traditional orthodontic treatments alone. SAPE can also improve the overall facial aesthetics of the patient by creating a more balanced and harmonious smile.
What is Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion?
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/ca/1×1.png
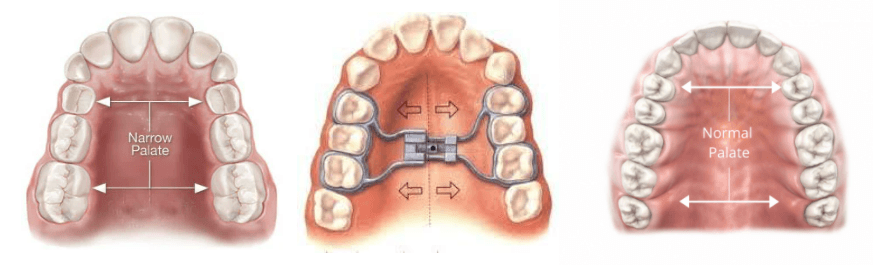
Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion (SAPE) is a dental procedure used to widen the upper jaw and create more space in the mouth. It is typically performed on individuals who have a narrow palate, which can lead to issues such as crowding of teeth, breathing difficulties, and speech problems.
The procedure involves making small incisions in the palate and inserting a device called a palatal expander. The expander is then gradually adjusted over a period of time to gradually widen the palate. This allows for the growth of new bone and the expansion of the upper jaw.
SAPE is often recommended for individuals who have completed their growth and development, as it is most effective in adults. However, it can also be performed on younger individuals if necessary.
During the procedure, the patient is typically under general anesthesia to ensure their comfort. The surgery itself is relatively quick, with most procedures taking around 30 minutes to an hour.
Overall, Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion offers a number of benefits for individuals with a narrow palate. It can help improve breathing, reduce the risk of dental problems, and improve speech. By widening the upper jaw, it creates more space in the mouth, allowing for proper alignment of the teeth and improved overall oral health.
Benefits of Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion
Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion (SAPE) is a procedure that offers several benefits for individuals with narrow palates or crowded teeth. This technique involves the use of a surgical intervention to widen the upper jaw and create more space for proper alignment of the teeth.
Here are some of the key benefits of surgically assisted palatal expansion:
| 1. Improved Dental Alignment |
By expanding the palate, SAPE allows for better alignment of the teeth. This can help resolve issues such as crowding, overlapping, or crooked teeth. Proper alignment not only enhances the appearance of the smile but also improves oral health and function. |
| 2. Enhanced Breathing and Sleep Quality |
Narrow palates can contribute to breathing difficulties, especially during sleep. SAPE helps widen the airway, allowing for improved airflow and reducing the risk of sleep apnea and snoring. This can lead to better sleep quality and overall well-being. |
| 3. Increased Chewing Efficiency |
With a wider palate, individuals can chew their food more efficiently. This can improve digestion and nutrient absorption, leading to better overall health. Additionally, proper chewing can help prevent issues such as indigestion and stomach discomfort. |
| 4. Enhanced Speech Function |
A narrow palate can affect speech clarity and pronunciation. SAPE can help widen the space in the oral cavity, allowing for better tongue movement and articulation. This can improve speech function and enhance communication skills. |
| 5. Long-Term Stability |
SAPE offers long-term stability for the results achieved. By surgically expanding the palate, the changes made are more permanent compared to non-surgical methods. This can help prevent relapse and ensure that the benefits of the procedure are maintained over time. |
Techniques for Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion
Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion (SAPE) is a procedure used to widen the palate in individuals with a narrow upper jaw. There are several techniques that can be used to perform SAPE, each with its own advantages and considerations.
1. Midline Palatal Split

2. Zygomatic Arch Distraction
3. Maxillary Osteotomy
Preparation for Surgically Assisted Palatal Expansion
Before undergoing surgically assisted palatal expansion, there are several important steps that need to be taken to ensure a successful procedure and smooth recovery. These preparations include:
- Consultation with a qualified oral and maxillofacial surgeon: It is crucial to schedule a consultation with a skilled surgeon who specializes in surgically assisted palatal expansion. During this appointment, the surgeon will evaluate your specific case, discuss the procedure in detail, and address any concerns or questions you may have.
- Medical evaluation: Prior to the surgery, a comprehensive medical evaluation will be conducted to assess your overall health and identify any potential risks or complications. This evaluation may include blood tests, imaging scans, and other diagnostic procedures.
- Dental examination: A thorough dental examination will be performed to assess the condition of your teeth, gums, and jaw. This examination will help determine the best approach for palatal expansion and ensure that your oral health is optimal before the surgery.
- Orthodontic preparation: In some cases, orthodontic treatment may be necessary before surgically assisted palatal expansion. This can involve wearing braces or other appliances to align the teeth and create sufficient space for the expansion.
- Pre-surgical instructions: Your surgeon will provide you with specific instructions to follow in the days leading up to the surgery. This may include guidelines regarding fasting, medication management, and other preparations to ensure a safe and successful procedure.
Recovery and Aftercare
During the first few days after the procedure, it is common to experience some discomfort, swelling, and bruising in the treated area. Pain medication prescribed by the surgeon can help manage any pain or discomfort. Applying ice packs to the face can also help reduce swelling.
Risks and Complications
Potential Risks

- Infection: There is a risk of developing an infection at the surgical site. This can usually be treated with antibiotics, but in some cases, additional surgical intervention may be required.
- Swelling and Bruising: Swelling and bruising are common after SAPE and typically subside within a few weeks. However, excessive swelling or bruising should be reported to the surgeon.
- Nerve Damage: There is a small risk of nerve damage during the procedure, which can result in numbness or tingling in the lips, tongue, or palate. In most cases, this is temporary and resolves on its own.
- Pain and Discomfort: Some pain and discomfort are to be expected after SAPE. Pain medication can be prescribed to manage any discomfort during the recovery period.
- Scarring: SAPE involves incisions in the palate, which can lead to scarring. However, the scars are usually not visible and do not cause any functional issues.
Possible Complications
- Delayed Healing: In some cases, the surgical incisions may take longer to heal than expected. This can be due to various factors, such as poor oral hygiene or underlying medical conditions.
- Relapse: There is a risk of relapse after SAPE, especially if the patient does not follow the post-operative instructions or wear a retainer as directed by the surgeon.
- Altered Sensation: In rare cases, SAPE can lead to permanent changes in sensation in the palate or surrounding areas. This can affect the ability to taste or chew food.

Dr. Fidel Cann: Esteemed orthodontist with a lifelong dedication to enhancing smiles and oral health. Pioneering expertise, compassionate care.